Linux 内核设计与实现 — 下半部
内核为处理中断提供了中断处理程序机制,这是内核必不可少的一部分。但仍然存在一些局 限:
- 中断程序异步执行,可能打断其它重要代码的执行;因此中断处理程序越快越好
- 正在处理中断的程序,最好的情况下,同级中断会被屏蔽;最坏情况下,所有中断都屏 蔽。禁止中断后,硬件无法与操作系统通信,因此中断处理程序越快越好
- 往往需要对硬件进行操作,所以有很高的时限要求
- 不在进程上下文运行,所以它们不能阻塞
这也就是为什么中断处理程序只能是中断处理流程的一部分的原因。因此中断处理流程的后 一部分称为 下半部 。
下半部
执行与中断处理密切相关但中断处理程序本身不执行的工作。理想情况下,中断处理程序将 所有工作交给下半部分执行。
上半部和下半部没有明显的划分界限,取决于驱动程序开发者自己。但有一些提示和借鉴:
- 如果一个任务对时间非常敏感,将其放在中断处理程序中
- 如果一个任务和硬件相关,将其放在中断处理程序中
- 如果一个要保证不被其它中断打断,将其放在中断处理程序中
- 其它所有任务,考虑放在下半部
环境
下半部不同与上半部,它可以有多种机制实现,分别由不同的接口和子系统组成。
起源
BH(bottom half) 机制:提供静态创建、32个 bottom halves 组成的链表,上半部通过一
个32位整数中的一位来标识出哪个 bottom half 可以执行。每个 BH 在全局范围内同
步,即使属于不同的处理器,也不允许人任何两个 bottom half 同时执行。
缺点是不够灵活,简单但有性能瓶颈。
任务队列
内核定义了一组队列,每个队列都包含一个由等待调用的函数组装成链表。驱动程序可以把 它们自己的下半部注册到合适的队列上去。
缺点还是不够灵活,无法替代整个 BH 接口;对于性能要求较高的子系统,如网络,它也
不能胜任。
软中断和 tasklet
软中断是一组静态定义的下半部接口,有 32 个,可以在所有处理器上同时执行,即使相同 类型也可以。
tasklet 是基于软中断实现的灵活性强、动态创建的下半部实现机制。不同类型的 tasklet 可以在不同的处理器上同时执行,相同类型则不行。
工作队列是一种比任务队列更有效的方法,先对推后执行的工作排队。已经取代了任务队列。 在 2.6 版本中,内核提供了软中断、tasklet 和工作队列三种机制。
软中断
用的比 tasklet 少,代码于 kernel/softirq.c 中。
实现
编译器静态分配的。定义于 include/linux/interrupt.h
struct softirq_action
{
void (*action)(struct softirq_action *);
};
内核定义了32该结构体的数组:
static struct softirq_action softirq_vec[NR_SOFTIRQS] __cacheline_aligned_in_smp;
软中断处理程序
当内核运行一个软中断处理程序的时候,就会执行这个 action 函数。只所以使用整个结
构体作为参数传递,是因为这样可以保证将来在结构体中加入新的域时,就不需要对所有的
软中断处理程序都进行变动。如果需要,也可以很方便的解析它的参数,从数据成员中提取
数据。
一个软中断不会抢占另外一个软中断,唯一可以抢占的是中断处理程序。
执行软中断
注册的软中断必须被标记后才会执行,称为触发软中断。通常中断处理程序返回前会标记它 的软中断。待处理软中断检查时机:
- 从一个硬件中断代码返回时
- 在 ksoftirqd 内核线程中
- 在那些显式检查和执行待处理的软中断的代码中,如网络子系统
都在 do_softirq() 中执行:
asmlinkage void __do_softirq(void)
{
struct softirq_action *h;
__u32 pending;
int max_restart = MAX_SOFTIRQ_RESTART;
int cpu;
pending = local_softirq_pending();
account_system_vtime(current);
__local_bh_disable((unsigned long)__builtin_return_address(0),
SOFTIRQ_OFFSET);
lockdep_softirq_enter();
cpu = smp_processor_id();
restart:
/* Reset the pending bitmask before enabling irqs */
set_softirq_pending(0);
local_irq_enable();
h = softirq_vec;
do {
if (pending & 1) {
unsigned int vec_nr = h - softirq_vec;
int prev_count = preempt_count();
kstat_incr_softirqs_this_cpu(vec_nr);
trace_softirq_entry(vec_nr);
h->action(h);
trace_softirq_exit(vec_nr);
if (unlikely(prev_count != preempt_count())) {
printk(KERN_ERR "huh, entered softirq %u %s %p"
"with preempt_count %08x,"
" exited with %08x?\n", vec_nr,
softirq_to_name[vec_nr], h->action,
prev_count, preempt_count());
preempt_count() = prev_count;
}
rcu_bh_qs(cpu);
}
h++;
pending >>= 1;
} while (pending);
local_irq_disable();
pending = local_softirq_pending();
if (pending && --max_restart)
goto restart;
if (pending)
wakeup_softirqd();
lockdep_softirq_exit();
account_system_vtime(current);
__local_bh_enable(SOFTIRQ_OFFSET);
}
使用
软中断是留给最严格以及最重要的下半部使用,目前就网络和 SCSI 子系统使用
分配索引
内核从 0 开始建立一种相对优先级,索引号小的先执行。

注册
调用 open_softirq() 注册软中断处理程序,参数为索引号和处理函数。
因为软中断可以同时运行其处理程序,因此任何共享数据都需要严格的锁保护。为了提高性 能,一般都放在一个处理器上运行,或其它一些技巧避免显加锁。
引入软中断的主要原因是其扩展性。如果不需要扩展到多个处理器,就可以直接使用 tasklet 了。
触发
在注册之后,新的软中断处理程序就能运行,调用 raise_softirq() 挂起软中断,在此
运行,通过 do_softirq() 触发。
tasklet
tasklet 比软中断有更广泛的用途。
实现
结构体
struct tasklet_struct
{
struct tasklet_struct *next;
unsigned long state;
atomic_t count; /* 引用计数 */
void (*func)(unsigned long);
unsigned long data; /* 参数 */
};
state 在 0 、TASKLET_STATE_SCHED、和 TASKLET_STATE_RUN 取值。
count 不为 0 则 tasklet 被禁止,不允许执行。只有为 0 时,才被即激活,并且在被设 置为挂起状态时,才能够执行。
调度
已调度(等同于触发的软中断)的 tasklet 存放在两个单处理器数据结构:
tasklet_vec(普通优先级) 和 tasklet_hi_struct(高优先级),斗士 tasklet 结构构成的链
表。分别由 tasklet_schedule() 和 tasklet_hi_schedule() 调度。
// tasklet_schedule
static inline void tasklet_schedule(struct tasklet_struct *t)
{
if (!test_and_set_bit(TASKLET_STATE_SCHED, &t->state))
__tasklet_schedule(t);
}
...
void __tasklet_schedule(struct tasklet_struct *t)
{
unsigned long flags;
local_irq_save(flags); // 保存中断状态
t->next = NULL;
*__this_cpu_read(tasklet_vec.tail) = t;
__this_cpu_write(tasklet_vec.tail, &(t->next)); // 添加到每一个处理器中 tasklet_vec 中
raise_softirq_irqoff(TASKLET_SOFTIRQ); // 唤起 TASKLET_SOFTIRQ, 下次调用 do_softirq 时会执行该 tasklet
local_irq_restore(flags); // 恢复中断状态
}
// tasklet_hi_schedule
static inline void tasklet_hi_schedule(struct tasklet_struct *t)
{
if (!test_and_set_bit(TASKLET_STATE_SCHED, &t->state))
__tasklet_hi_schedule(t);
}
...
void __tasklet_hi_schedule(struct tasklet_struct *t)
{
unsigned long flags;
local_irq_save(flags);
t->next = NULL;
*__this_cpu_read(tasklet_hi_vec.tail) = t;
__this_cpu_write(tasklet_hi_vec.tail, &(t->next));
raise_softirq_irqoff(HI_SOFTIRQ);
local_irq_restore(flags);
}
tasklet 处理的核心函数是 tasklet_action 和 tasklet_hi_action:
static void tasklet_action(struct softirq_action *a)
{
struct tasklet_struct *list;
local_irq_disable(); // 禁止中断
list = __this_cpu_read(tasklet_vec.head); // 检索当前 cpu 的 tasklet_vec
__this_cpu_write(tasklet_vec.head, NULL); // 检索保存后将 tasklet_vec 置 NULL
__this_cpu_write(tasklet_vec.tail, &__get_cpu_var(tasklet_vec).head);
local_irq_enable(); // 允许中断响应
while (list) {
struct tasklet_struct *t = list;
list = list->next;
if (tasklet_trylock(t)) {
if (!atomic_read(&t->count)) { // 检查 count 是否为 0,确保没有被禁止。如果是多处理器,在这之前还需检查 TASKLET_STATE_RUN
if (!test_and_clear_bit(TASKLET_STATE_SCHED, &t->state))
BUG();
t->func(t->data);
tasklet_unlock(t);
continue;
}
tasklet_unlock(t);
}
local_irq_disable();
t->next = NULL;
*__this_cpu_read(tasklet_vec.tail) = t;
__this_cpu_write(tasklet_vec.tail, &(t->next));
__raise_softirq_irqoff(TASKLET_SOFTIRQ);
local_irq_enable();
}
}
// tasklet_hi_action 类似, 不再重复
使用
声明 tasklet
可以静态也可以动态创建。
编写处理程序
必须用锁适当保护与中断或相同 tasklet 之间的共享数据。
调度
调用 tasklet_schedule() 调度。 tasklet_disable() 用来禁用 tasklet,如果
tasklet 正在运行,则等其执行完在返回。 tasklet_disable_nosync() 不用等待执行完
毕就禁止,这样一般不太安全。 tasklet_enable() 激活 tasklet. tasklet_kill()
用于从挂起的队列去掉一个 tasklet.
ksoftirqd
每个处理器都有一组辅助处理软中断的内核线程。
工作队列
可以把工作推后,交由一个内核线程去执行,这样这个下半部分总会在进程上下文中执行。 占据进程上下文的优势。而且还允许重新调度甚至睡眠。
实现
数据结构
/*
* 外部可见的工作队列抽象是由每个工作队列组成的数组
*/
struct workqueue_struct {
unsigned int flags; /* I: WQ_* flags */
union {
struct cpu_workqueue_struct __percpu *pcpu;
struct cpu_workqueue_struct *single;
unsigned long v;
} cpu_wq; /* I: cwq's */
struct list_head list; /* W: list of all workqueues */
struct mutex flush_mutex; /* protects wq flushing */
int work_color; /* F: current work color */
int flush_color; /* F: current flush color */
atomic_t nr_cwqs_to_flush; /* flush in progress */
struct wq_flusher *first_flusher; /* F: first flusher */
struct list_head flusher_queue; /* F: flush waiters */
struct list_head flusher_overflow; /* F: flush overflow list */
mayday_mask_t mayday_mask; /* cpus requesting rescue */
struct worker *rescuer; /* I: rescue worker */
int saved_max_active; /* W: saved cwq max_active */
const char *name; /* I: workqueue name */
#ifdef CONFIG_LOCKDEP
struct lockdep_map lockdep_map;
#endif
};
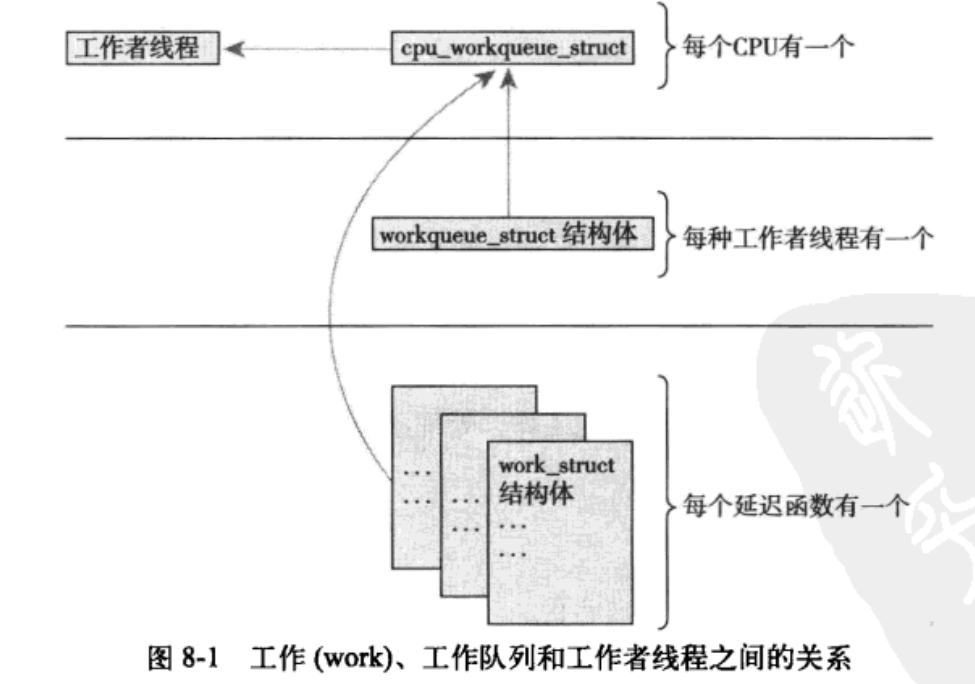
每个工作者线程对应一个 cpu_workqueue_struct 结构。
struct cpu_workqueue_struct {
struct global_cwq *gcwq; /* I: the associated gcwq */
struct workqueue_struct *wq; /* I: the owning workqueue */
int work_color; /* L: current color */
int flush_color; /* L: flushing color */
int nr_in_flight[WORK_NR_COLORS];
/* L: nr of in_flight works */
int nr_active; /* L: nr of active works */
int max_active; /* L: max active works */
struct list_head delayed_works; /* L: delayed works */
};
工作的数据结构
struct work_struct {
atomic_long_t data;
struct list_head entry;
work_func_t func;
#ifdef CONFIG_LOCKDEP
struct lockdep_map lockdep_map;
#endif
};
这些结构被连接成链表,在每个处理器上的每种类型的队列都对应这样的一个链表。
每个工作线程都要执行 worker_thread() 函数,有操作插入到队列就唤醒,当队列为空
时就休眠。
工作队列总结
使用
创建推迟的工作
通过对应的宏来创建并初始化工作队列。
处理函数
该函数会运行在进程上下文,默认允许响应中断,并且不支持任何锁。如果需要,可以睡眠。 需要注意的是不能访问用户空间。因为内核线程在用户空间没有相关的内存映射。
调度
schedule_work(&work) 进行调度。
不希望工作马上执行,可以用 schedule_delayed_work() 延迟指定时间。
刷新
排入队列的工作会在工作线程下一次唤醒时执行。有时在下一步工作之前必须保证一些操作 已经完成,所以内核准备了一个刷新指定队列的函数:
void flush_schedule_work(void)
取消延迟, int cacel_delayed_work(struct work_struct *work)
创建新的工作队列
默认的不满足,就只能自己创建,需创建一个工作队列和相应的工作者线程。
struct workqueue_struct *create_workqueue(const char *name)
还有其它相应的一些函数就不列举了。
下半部机制选择

